@input, @output & EventEmitter In Angular
In this article, we will learn how to use @input, @output, and EventEmitter in Angular. These decorators are used to send data from the parent component to the child component and vice versa. @Input specifies the component's input property, which can be changed by the parent component. The @output specifies the output property (event), which is raised by the EventEmitter in the child component. These occurrences are relayed to the parent.
@input, @output & Eventemitter
@input
The input decorator transforms a property into an input property. That is, it is capable of receiving data from the parent component. Property binding is used by the parent component to connect it to a component property. Angular updates the value in the child component whenever the value in the parent component changes.
Example
Consider the component class below:
@Component({
selector: 'app-customer-detail',
templateUrl: './customer-detail.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./customer-detail.component.css']
})
export class CustomerDetailComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() customer:Customer;
}
<app-customer-detail customer="" selectedcustomer=""></app-customer-detail>
@output
Example
//Declare the property
@Output() customerChange:EventEmitter<customer> =new EventEmitter<customer>();
//Raise the event to send the data back to parent
update() {
this.customerChange.emit(this.customer);
}
<app-customer-detail customer="" customerchange="" event="" selectedcustomer="" update=""></app-customer-detail>
EventEmitter
//Define output property
@Output() customerChange:EventEmitter<customer> =new EventEmitter<customer>();
//Raise the event using the emit method.
update() {
this.customerChange.emit(this.customer);
}
@input, @output & Eventemitter Example
ng new InputOutputExample cd InputOutputExample
Create the components customerList and customerDetail. Create a customer class as well.
ng g c customerList ng g c customerDetail ng g class customer
Create customer class.
export class Customer {
customerNo: number=0;
name: string="";
address: string="";
city: string="";
state: string="";
country: string="";
}
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { CustomerListComponent } from './customer-list/customer-list.component';
import { CustomerDetailComponent } from './customer-detail/customer-detail.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
CustomerListComponent,
CustomerDetailComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
FormsModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
})
export class AppModule { }
Child Component
import { Component, OnInit, Input, Output,EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
import { Customer } from '../customer';
@Component({
selector: 'app-customer-detail',
templateUrl: './customer-detail.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./customer-detail.component.css']
})
export class CustomerDetailComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() customer:Customer = new Customer();
@Output() customerChange:EventEmitter<customer> =new EventEmitter<customer>();
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
update() {
this.customerChange.emit(this.customer);
}
}
@Input() customer:Customer = new Customer();
customerChange is an output property of the EventEmitter type.
@Output() customerChange:EventEmitter<customer> =new EventEmitter<customer>();
We raise the event customerChange whenever the user changes the customer. We provide it the updated customer as an argument.
update() {
this.customerChange.emit(this.customer);
}
The following code is the customer-detail.component.html file.
<p>Customer No : {{customer.customerNo}}</p>
<p>Name : <input customer.name="" ngmodel="" /></p>
<p>Address : <input customer.address="" ngmodel="" /></p>
<p>city : <input customer.city="" ngmodel="" /></p>
<p>state : <input customer.state="" ngmodel="" /></p>
<p>country : <input customer.country="" ngmodel="" /></p>
<button click="" update="">Update</button>
Parent Component
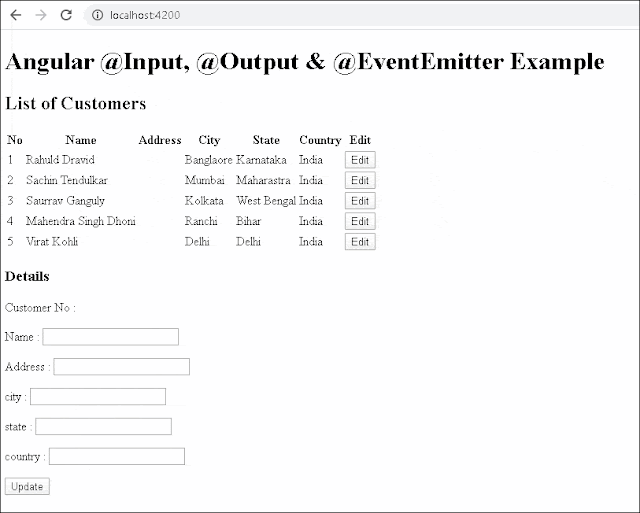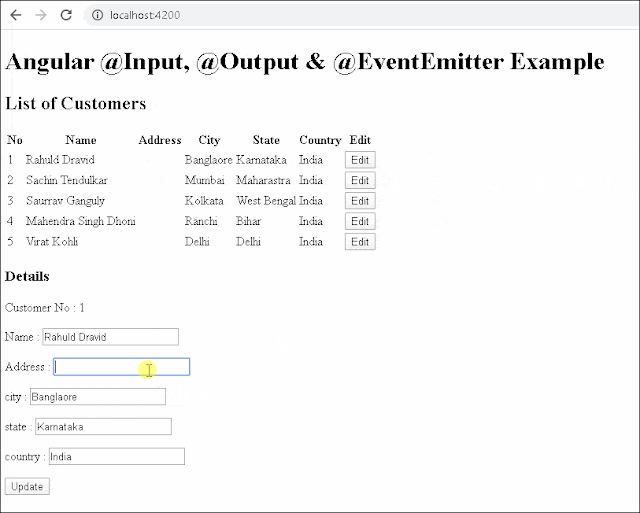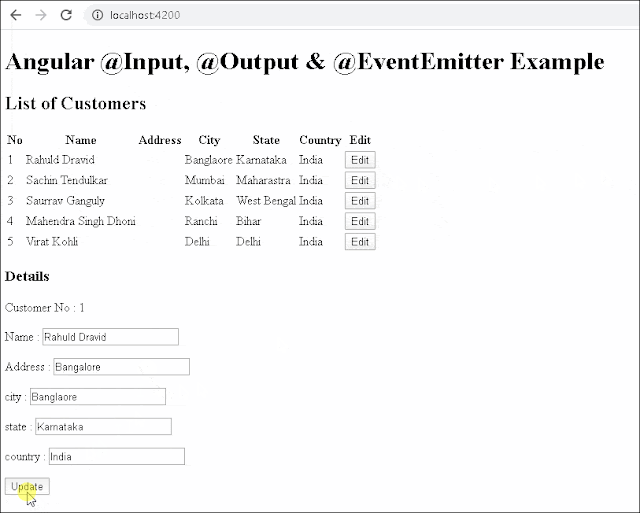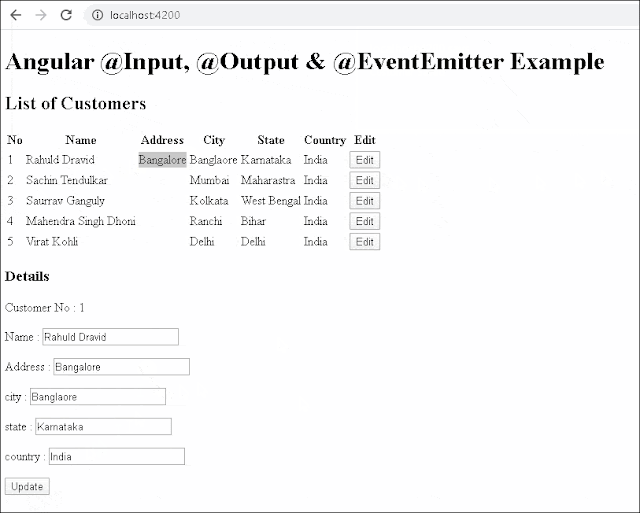
<h2>List of Customers</h2>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>No</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>State</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Edit</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr ngfor="let customer of customers;">
<td>{{customer.customerNo}}</td>
<td>{{customer.name}}</td>
<td>{{customer.address}}</td>
<td>{{customer.city}}</td>
<td>{{customer.state}}</td>
<td>{{customer.country}}</td>
<td><button click="" customer="" showdetails="">Edit</button></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Details</h3>
<app-customer-detail customer="" customerchange="" event="" selectedcustomer="" update=""></app-customer-detail>
<button click="" customer="" showdetails="">Edit</button>
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Customer } from '../customer';
import { element } from 'protractor';
import { ObjectUnsubscribedError } from 'rxjs';
@Component({
selector: 'app-customer-list',
templateUrl: './customer-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./customer-list.component.css']
})
export class CustomerListComponent implements OnInit {
customers: Customer[] = [
{customerNo: 1, name: 'Rahuld Dravid', address: '', city: 'Banglaore', state: 'Karnataka', country: 'India'},
{customerNo: 2, name: 'Sachin Tendulkar', address: '', city: 'Mumbai', state: 'Maharastra', country: 'India'},
{customerNo: 3, name: 'Saurrav Ganguly', address: '', city: 'Kolkata', state: 'West Bengal', country: 'India'},
{customerNo: 4, name: 'Mahendra Singh Dhoni', address: '', city: 'Ranchi', state: 'Bihar', country: 'India'},
{customerNo: 5, name: 'Virat Kohli', address: '', city: 'Delhi', state: 'Delhi', country: 'India'},
]
selectedCustomer:Customer = new Customer();
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {
}
showDetails(customer:Customer) {
this.selectedCustomer=Object.assign({},customer)
}
update(customer:Customer) {
console.log(customer)
var cust=this.customers.find(e => e.customerNo==customer.customerNo)
Object.assign(cust,customer)
alert("Customer Saved")
}
}
<app-customer-list></app-customer-list>
Notes on @Input & @Output
@Input(‘customerData’) customer:Customer;
Intercept input property changes with a setter
private _customerData = '';
@Input()
set customer(customer: Customer) {
//You can add some custom logic here
this._customerData = customer;
console.log(this._customerData)
}
get customer(): string { return this._customerData; }